Mynabay.com - The DCC Monitor Project
Building a DCC Monitor with an Arduino
MynaBay is developing an Arduino library for model railroad DCC projects. DCC monitors, accessory decoders and even mobile decoders can be built using the Arduino. This source code is being given to the model railroad world as public domain. You're free to do whatever to want, using this as a starting point. Our plan is continue to expand the library and add more examples.
DCCInterface.com
** DCCInterface.com produces Arduino boards that work with this library. Contact them for details on their hardware.
Github.com
Code : https://github.com/MynaBay/DCC_Decoder
To begin, you'll need to install the Arduino IDE from www.arduino.cc. You'll find the download and complete instructions for your environment there. It's recommended that you install the IDE and run some of the default examples on an Arduino before tackling the DCC Monitor.
DCC specifications contain DCC packet format details. Visit NMRA.org for more details.
The DCC Monitor will parse the DCC signal and count packets. Every two seconds the data is dumped out the serial monitor on your computer.
We built a DCC monitor using an Arduino Uno and a few components.
This article will walk you through how we built it.
Arduinos and parts can be found on Amazon.com, see the links in righthand column. Digi-Key is a great place to purchase the optoisolator, diode and resistors.

Parts Needed:
[ 1 ] Arduino Uno
[ 1 ] Small breadboard
[ 2 ] 10K resistors
[ 1 ] 1K resistor
[ 1 ] Diode 1N4148
[ 1 ] Optoisolator 6N137
[ 6 ] Jumper wires

We'll start by building this circuit. A big thanks to Dave Falkenburg for providing this circuit to us. It made this project possible.

The DCCIN connections are the two rails where you want to monitor the DCC signal. This signal is run through an optoisolator (6N137). This protects the Arduino from the higher voltages on the rails. The output of the optoisolator is connected to pin 2 on the Arduino. This pin drives interrupt 0 on the Arduino, software takes it from there.
We'll be building this circuit on the breadboard and connecting to the Arduino Uno.
Step 1
Place the optoisolator on the breadboard. Pin 1 has a little dot above it.

Step 2
Place the diode between pins 2+3 on the optoisolator. The orientation of a diode matters. Make sure you have it facing the right direction.

Step 3
Place the 1K resistor from pin 2 to an unused slot.

Step 4
Insert a small jumper from pin 8 to an unused slot. This slot we'll refer to a +5v.

Step 5
Place a 10K resistor between pin 7 and +5v slot from step 4.

Step 6
Place the other 10K resistor between pin 6 and +5v slot.

Step 7
Place jumpers (we used red) to attach to the input signal. One on pin 3 and the other to the unused slot from step 3. These are the connection to DCC signal, or simply the rails.

Step 8
Attach a jumper (we used orange) to attach to +5v on the Arduino.

Step 9
Attach a jumper (we used green) to pin 5. This will attach to gnd on the Arduino.

Step 10
Attach a jumper (we used blue) to pin 6. This will attach to interrupt on Arduino.

Step 11
Attach interrupt jumper (blue) to pin 2 on the Arduino.

Step 12
Attach +5v jumper (orange) to 5v on Arduino.

Step 13
Attach gnd jumper (green) to GND on Arduino.

Step 14
Attach jumper wires to the rails where a DCC signal will be present. The rails are not shown in photo but they're on the other end of the clip leads. We tested this with our NCE system.

At this point your hardware is assembled and ready to go. On to the software.
Step 15
Download and install our DCC_Decoder library. The download is in a zip file. In general, you'll unzip this to get the DCC_Decoder directory. Copy this directory to the libraries directory inside the sketchbook location. The libraries directory may not exist and you'll need to create one. See the preferences in the Arduino IDE for the sketchbook directory location. Place the DCC_Decoder directory (not .zip file, it's unzipped contents) inside the directory named libraries. See the Arduino site for more information on installing a library.
Step 16
Attach the Arduino to your platform with the USB cable. No photo, but a simple step.
Step 17
Launch Arduino IDE and choose the DCC_Monitor example. If DCC_Decoder isn't there you might need to restart Arduino IDE or the library isn't installed correctly. Go back to step 15.

Step 18
Upload the sketch to your Adruino.

Step 19
Wait for upload to finish.

Step 20
Open the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE.

Step 21
Turn on the DCC booster and watch packet data in monitor window.
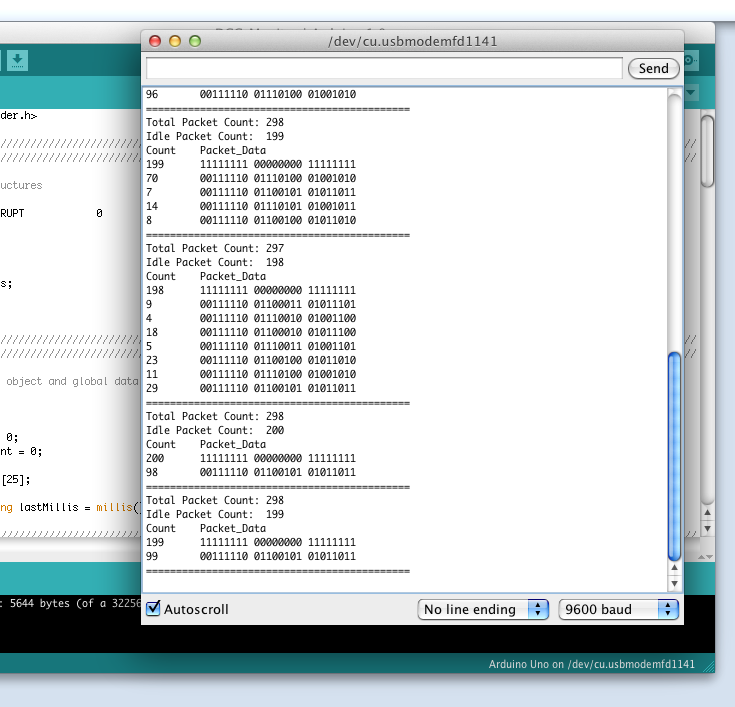
That's it...Enjoy your DCC monitor.
Source : https://www.mynabay.com/dcc_monitor
DCC Sniffer Arduino Monitor Mynabay